
| Company | Role | Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Statflo | Product Manager | User Interviews |
| Journey Mapping | ||
| Market Research | ||
| Data Analysis |
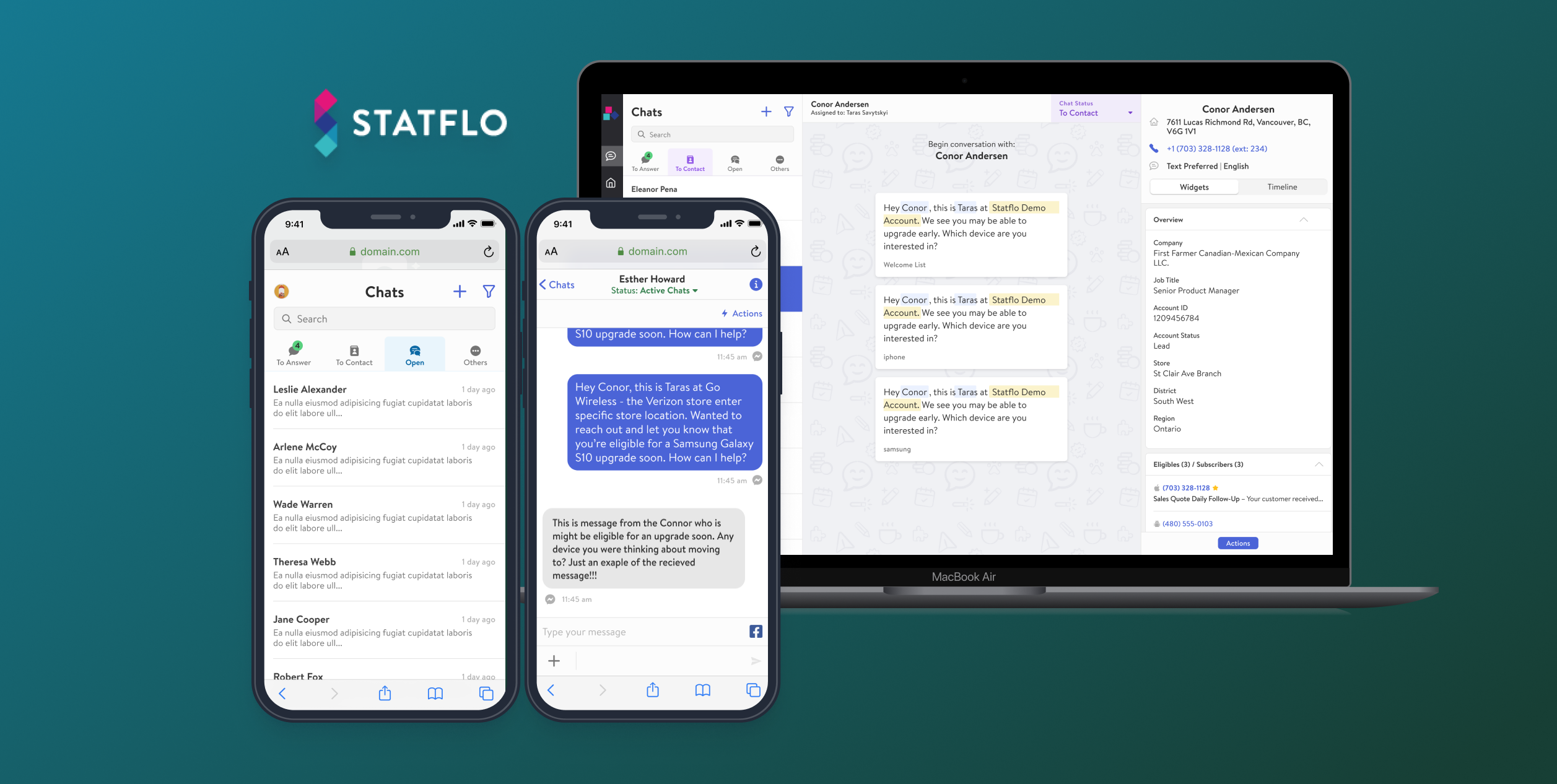
As a result of the global pandemic, companies prioritized diversifying and stabilizing their revenue streams. For Statflo, after conducting market research, it was determined that the financial services industry would be the next ideal vertical to pursue. After conducting thorough user research, the functionality to receive inbound SMS messages from unrecognized phone numbers was delivered, enabling the targeted growth in the company’s annual recurring revenue.
Statflo is a B2B software company that is revolutionizing how retail businesses pursue and execute sales across their organization. Their business messaging product enables sales representatives to build authentic relationships with existing customers and conduct outreach campaigns better. In a retail business context, an outreach campaign is a sales strategy that involves initiating contact with existing and prospective customers to identify individuals who may be interested in making a purchase. Via processing customer and transactional data through machine learning algorithms, sales representatives are given guidance on the best potential customers to contact, recommended active sales campaigns to mention, and advised on how best to phrase every message.
I was employed at Statflo soon after the global pandemic, which amplified the importance of a diversified and reliable revenue stream, particularly for smaller companies. As a result, the Product Management department was tasked with acquiring clients in a new industry sector and increasing overall recurring revenue. After conducting market research and consulting with stakeholders, the financial services industry was determined to be the primary industry to pursue. The team then conducted thorough user research to identify which feature would best enable penetration into the financial services space.
As with most companies, the responsibilities of a product manager at Statflo spanned the entire product lifecycle, intending to generate the greatest possible business value. Seeing as how the role of a product manager is to create products that provide business value, the products they create can then be evaluated upon the sales and profits they generate. This demands technical expertise and a business aptitude. The actual responsibilities included, but were not limited to strategy definition, requirements management, solution ideation, stakeholder management, and release cycle planning. A lack of effective product management could result in repercussions such as customer dissatisfaction or scope creep. For B2B companies, this entails financial penalties and impacts on sales.
Before delving into the design methods, it is important to note that a large portion of the following process was executed collaboratively, or at the very least, involved receiving feedback from essential stakeholders. Before initiating any development, it is imperative for the product manager to facilitate the formation of a team, which should include members from various roles such as marketing, sales, customer support, quality assurance, project management, and software engineering. An external source of feedback to consider as well is a prospective client. Rather than creating a feature that fulfils the perceived needs of a market, a B2B company can somewhat guarantee revenue by establishing a relationship with a sizeable potential client and explicitly addressing their known needs. This can also indirectly lead to satisfying the general needs of the market. All core team members are expected to contribute to decision-making processes with insights they have accrued, such as from interactions with potential and existing customers or from historical project knowledge. The diversity of the core team ensures the consideration of contrasting perspectives, but the onus of the final decision remains on the product manager. When working with such a cross-functional team, a common issue that must be mitigated by the product manager is the description of requirements lacking varied abstraction levels for different stakeholders; potentially causing ambiguity and suboptimal decision-making.
The first pivotal step in the product development process was to conduct extensive market research in the retail bank industry. Market research yields quantitative and qualitative data about the market, which consists of potential customers, competitors, and analysts. A product manager's ongoing market research can also be supplemented with insights from core team members such as those in marketing or sales.
Immediately following the market research was preliminary user research. Although a great amount of time was spent conducting market research, even more time was spent conversing with individuals from the retail bank industry. User research is more essential than market research for building a successful product because most software product failures are due to a lack of user input. Having this emphasis on maintaining a user-centric perspective minimizes the occurrence of uninformed ad-hoc decision-making. Unfortunately, like most product management activities, there is no prescribed approach to conducting user research. However, several widely accepted tools can be leveraged such as user interviews, user observations, or distributed surveys, all of which were used in the Statflo Product Management Department. User interviews involve asking open-ended questions and prompting users to describe current workflows, highlighting any frustrations, and revealing current workaround measures. In conducting an interview, it is imperative to record and transcribe the interview while requesting clarifications where appropriate to funnel down to the root cause of certain issues. The interviewee demographic can vary greatly, ranging from casual product users to members of a carefully crafted customer advisory panel. Customer advisory panels are an excellent source of knowledge for a product manager, typically composed of enthusiastic users who hope to contribute by positively influencing product development. It is imperative to select optimal interviewees since poor insights will directly yield a suboptimal product. This is all done to ideate potential problem spaces to address. User observations are conducted to understand user behaviour in a natural workflow, which could reveal insights that the user is not consciously aware of. Distributed surveys allow product managers to interview a plethora of users simultaneously to gather standardized and structured data that can complement findings from user interviews.
Following the completion of preliminary research, a problem space must be selected and adequately defined. Although there were several potential problem spaces identified from the research in the retail bank industry, it was unrealistic to address more than one at a time for an individual contributor. Ergo, the problem spaces needed to be prioritized. One such way to accomplish this was through Kano Modelling. In a Kano Model, problem spaces are relatively mapped onto a graph based on customer satisfaction and functionality, following three prominent curves: the Attractive, One-Dimensional, and Must-Be curves. Problem spaces on the Attractive curve are predicted to provide users with the greatest satisfaction whereas the One-Dimensional curve provides a proportional and reasonable level of satisfaction, and the Must-Be curve represents problem spaces that absolutely must be addressed. For a product management team, it is ideal to pursue a few problem spaces from every curve on the Kano Model to appease current users while still ensuring the product remains competitive in the future market. The placement of a particular problem space is determined through the cumulative results of user interviews or distributed surveys where individuals are asked qualitative and quantitative questions regarding their perceived importance of the problem spaces. A sample Kano model is illustrated below.
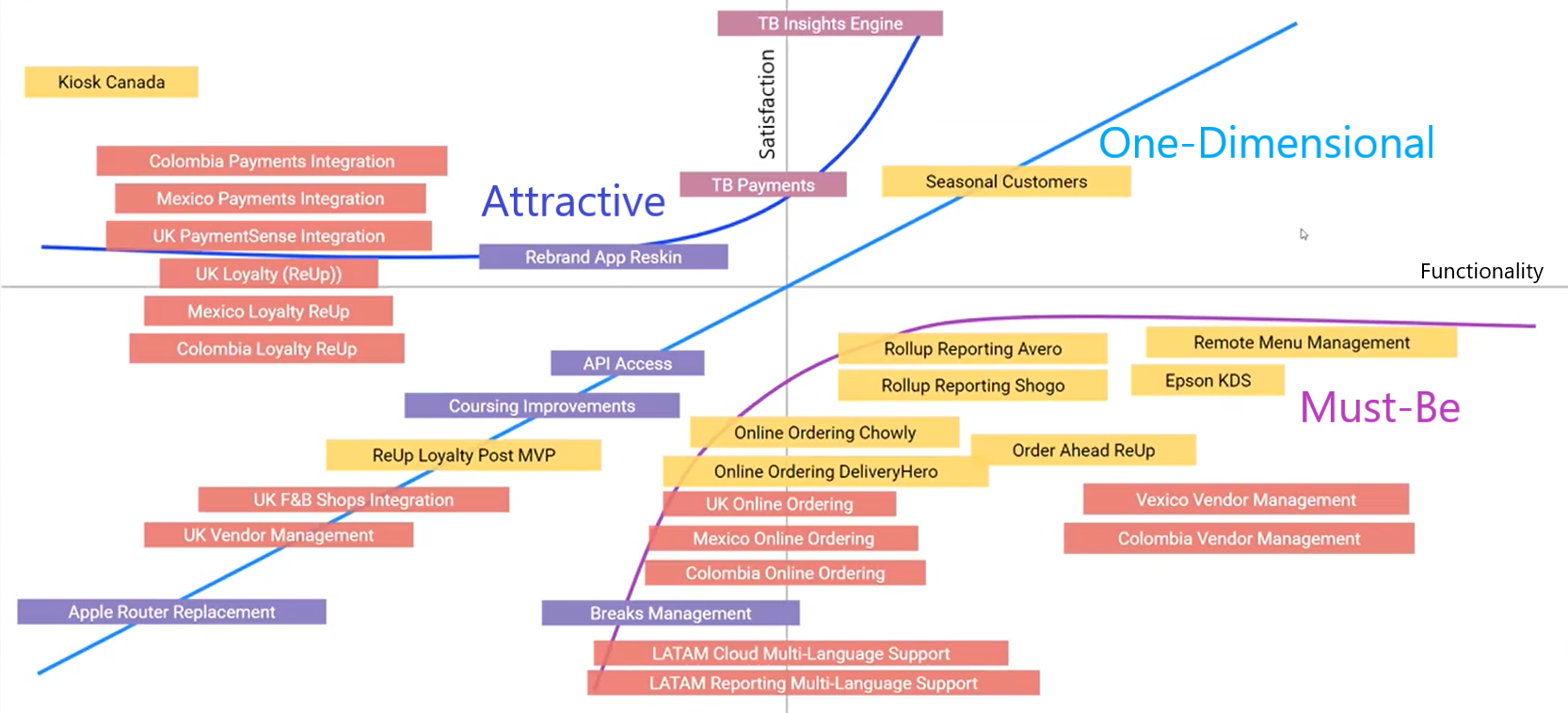
This could be accomplished by creating a Python script that parses through the transcripts of every user interview conducted in the previous fiscal quarter. By searching for keywords and phrases associated with the listed problem spaces, a continuous count can indicate the frequency with which a problem space was mentioned across interviews. The output is then a list of Must-Be problem spaces in order of popularity with users, with the most popular one being the ideal problem space to pursue. At that point, the most popular Must-Be problem space was regarding the inability to receive inbound short message service (SMS) messages from unrecognized phone numbers. Based on the research, there was a substantial number of prospective customers who were frustrated with their inability to text a local retail bank for general inquiries or promotional offers. In this context, unrecognized phone numbers referred to phone numbers that were not associated with an existing customer in a client’s database, and the person associated with an unrecognized phone number was defined as a lead. For all Statflo-internal communications, the problem space was referred to as Inbound SMS.
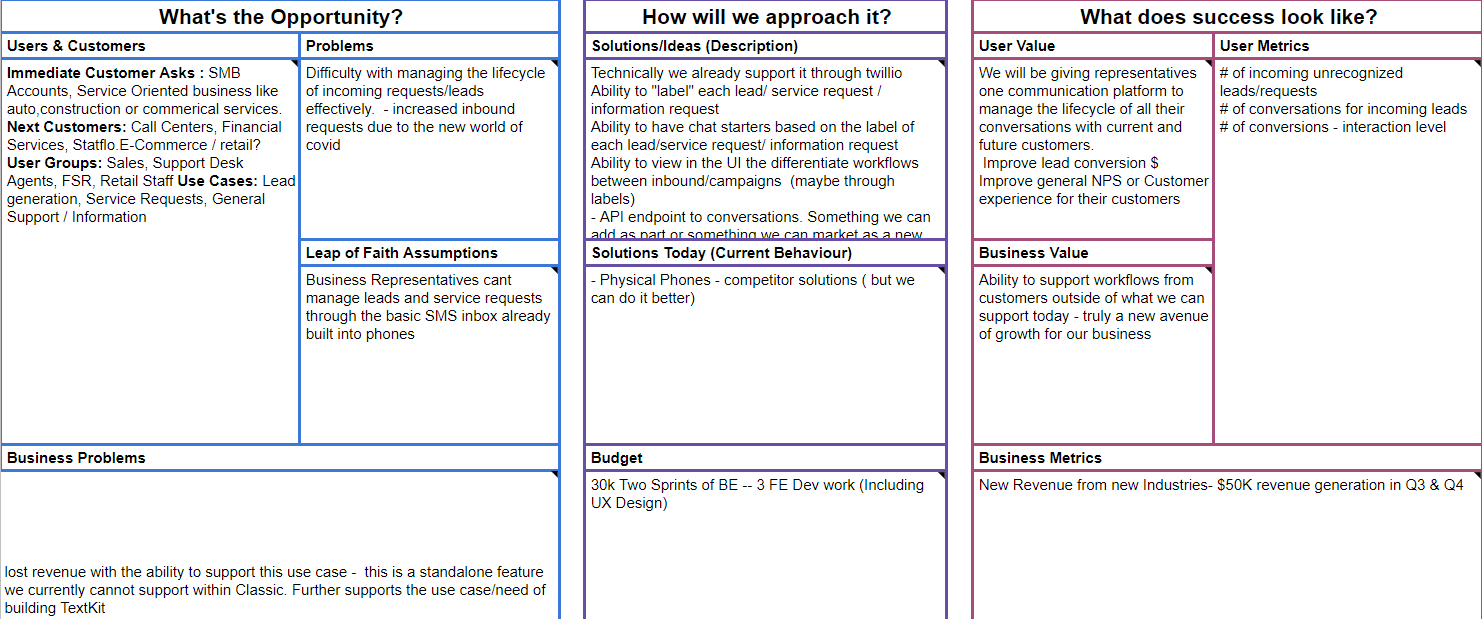
After homing in on a problem space, leveraging all the insights conducted from market and user research culminates in the form of a business canvas. The business canvas is a tool used by product managers to clarify the problem space and advocate for the business value that can be unlocked. Through business canvases, questions about the unresolved problem, business value, user value, and existing solutions are addressed. If a feature is developed without business rationale, the requirements of the feature will inevitably continuously change. A completed business canvas is then presented for approval to pivotal internal stakeholders such as the Board of Directors, who are responsible for defining the company’s overall strategy, vision, and mission. A preliminary draft of the business canvas is shown below.
Upon receiving approval to pursue a certain problem space, gathering more granular user research was required. Preliminary research was conducted to determine the optimal problem space to address, whereas more granular research highlights the actual pain points within the problem space, and determines what functionality is critical for the launched feature to be of any value. For example, the feature of enabling voicemails on smartphones would provide no value if the ability to play back a recorded voicemail was not included. Similar means as mentioned above for preliminary user research can be used to conduct the granular research. The caveat is that the scope of questions being asked should be narrowed to pertain only to the defined problem space to discover the most important aspects of the relevant workflow. All the insights gathered from granular user research can then be summarized in the form of user personas, which are fictional representations of actual users. Personas can serve as a reference point when making pivotal product decisions and rationalizing the development of certain functionality within a larger feature.
To ensure a successful feature launch, it is imperative to vet and prioritize the ideated functionalities that were produced from the granular user research. It is the role of the product manager to identify a few functionalities that uniquely characterize the feature, a concept commonly referred to as the minimum viable product (MVP). The product manager can then select the optimal subset of functionality suites to be developed in iterations of the feature by considering functionality interdependencies and other factors. Suboptimal organizing and sequencing of functionality suites can result in the loss of market share or budget overruns due to delayed launches, so it is a high-risk task. Although several tools can be used for functionality prioritization, the vast majority fail to sufficiently consider user value. A few collaborative tools that do account for user value are the Buy-a-Feature and MoSCoW techniques. The Buy-a-Feature technique involves gathering all essential internal and external stakeholders in a room and providing them with a fictional budget. They are then asked to visit checkpoints around the room that describe different proposed functionalities as well as their fictional prices. In the MoSCoW technique, internal and external stakeholders are asked to assign functionalities to the following categories: Must Do, Should Do, Could Do, and Won’t Do. In both techniques, the functionalities are prioritized and thus a general phasing plan of functionality suites is produced unless certain interdependencies exist.
From the prioritization results, a visual phasing plan can then be constructed by the product manager to better facilitate subsequent feedback discussions. The phasing plan can be illustrated in several ways, but a user story map is a commonly used tool that highlights the essential interaction points between a user and a product. In a user story map, functionalities are vertically aligned to a certain section of the user workflow and horizontally aligned to a certain feature release iteration. This is illustrated below.

The use of a story map synthesizes and leverages findings from user research via the perspective of a persona to effectively empathize with the user and thus optimize the product’s chance for market success. It also indirectly raises awareness of finer details in the workflow.
A stakeholder group that provides functionality prioritization feedback differently is the software engineering department. Once these stakeholders are walked through a story map, they are expected to comment on the feasibility of delivering certain functionalities within specified timelines as well as any technical interdependencies to consider. It is also important to note that feedback from stakeholders is not weighed equally. In general, functionality phasing plans can be affected by several factors such as company maturity, prestige or marketability of a potential client, geographic location of a potential client, resource availability, the size of a contract, or whether a contractual obligation has already been made. It would be illogical for Statflo, as a mid-sized company, to cater to the needs of a particular client if it comes at the cost of losing a contract with a significantly larger client.
All the work of the product manager culminates in the product requirements document, which is the one source of truth for all internal stakeholders in the development process. The document encapsulates key concepts such as the feature’s relevance to the company’s strategy and vision, the functionality phasing plan, and important research findings that inspired the feature. In some cases, low-fidelity wireframes can also be included.
At this point in the process, the product manager collaborates with a marketing team to ideate on how best to position and market the feature launch to penetrate the market. A key consideration is that the marketing strategy of the feature must complement the marketing strategy of the overall product and company. The product manager also simultaneously collaborates with a quality assurance team to ensure that all testing scenarios are considered in a predetermined testing suite. In addition, the product manager may also collaborate with a product designer to ensure that the necessary wireframes are created to provide software developers with a reference during interface development.
In the software development stage, most of the responsibilities begin to shift from the product manager to the project manager. In most software organizations, development teams follow Scrum methodology, where software is incrementally developed in timeboxed ‘sprints’. This practice aligns with the aforementioned intention of creating an MVP and incrementally improving upon it. Through adopting Scrum ceremonies, it is also practical to transition seamlessly from the more abstract user story map to the prioritized backlog of development work. For the backlog, the product manager is not simply describing intended functionality, but rather translating business objectives and aligning perspectives from the user’s point of view. In other words, a user story condenses research findings into a sentence with three components: the targeted persona, their need, and the rationale for the need. However, to obtain a refined backlog, a refinement meeting must occur where the product manager ensures the proposed work is feasible and understandable, which often requires the planning of system architecture and the distribution of engineering tasks.
Due to superb project management, all the functionality included in the MVP phase was launched on time. Concerning the first section of the user workflow, leads were appropriately assigned to sellers, and sellers were able to identify and prioritize conversations with leads. In terms of message scanning, inappropriate inbound and outbound messages were censored, and phone numbers were constantly checked against a client’s customer database. For concluding conversations, sellers could dismiss conversations and add a lead’s contact information to a customer database. Finally, for post-interaction activities, sellers were able to block certain customers and conduct follow-up campaign activities. Of the launched MVP functionalities, two were recognized as being critical for users from the prioritization techniques. These were the ability to add a lead’s contact information to a customer database, and the ability to filter for conversations with inbound leads, both of which are shown in the two wireframes below.
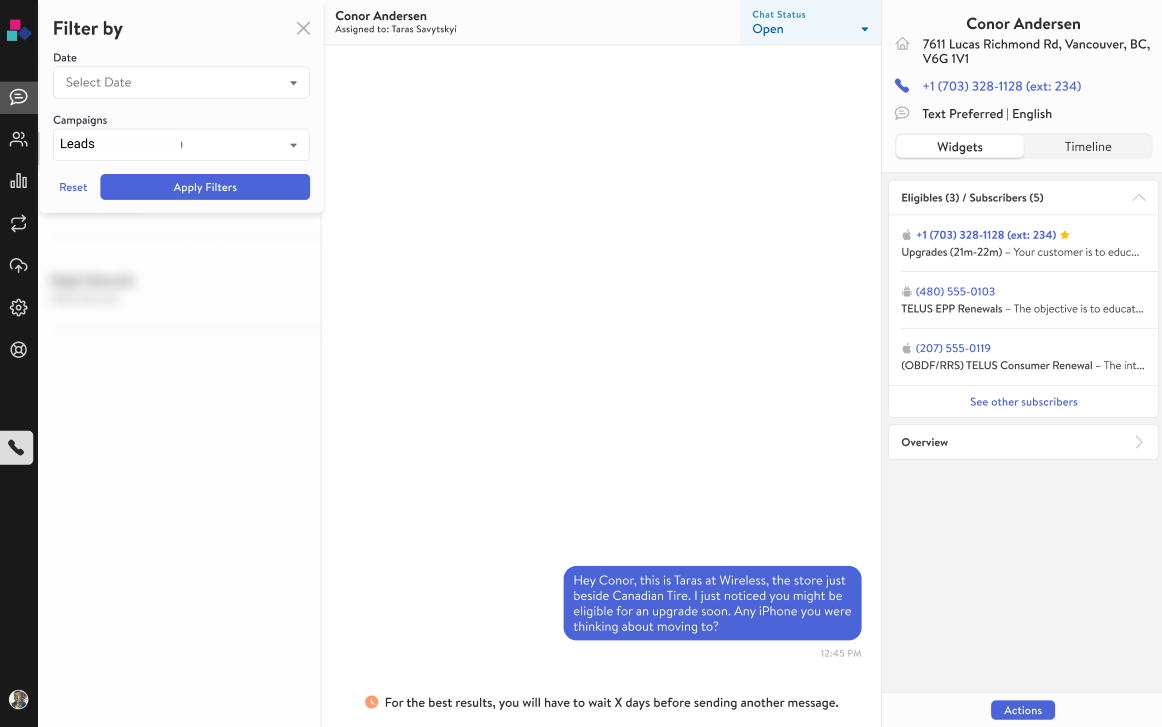
The wireframe above illustrates the desktop view of the TextKit product. The ability to filter for and prioritize conversations with leads was identified as being critical for retail banks because this was a major revenue source. Based on user research, it was found that a significant portion of a retail bank’s revenue originated from customers who initiated contact and inquired about the bank’s services. This dwarfed the revenue that banks would obtain from conducting outreach campaigns, so sellers needed to be able to prioritize conversations with leads.
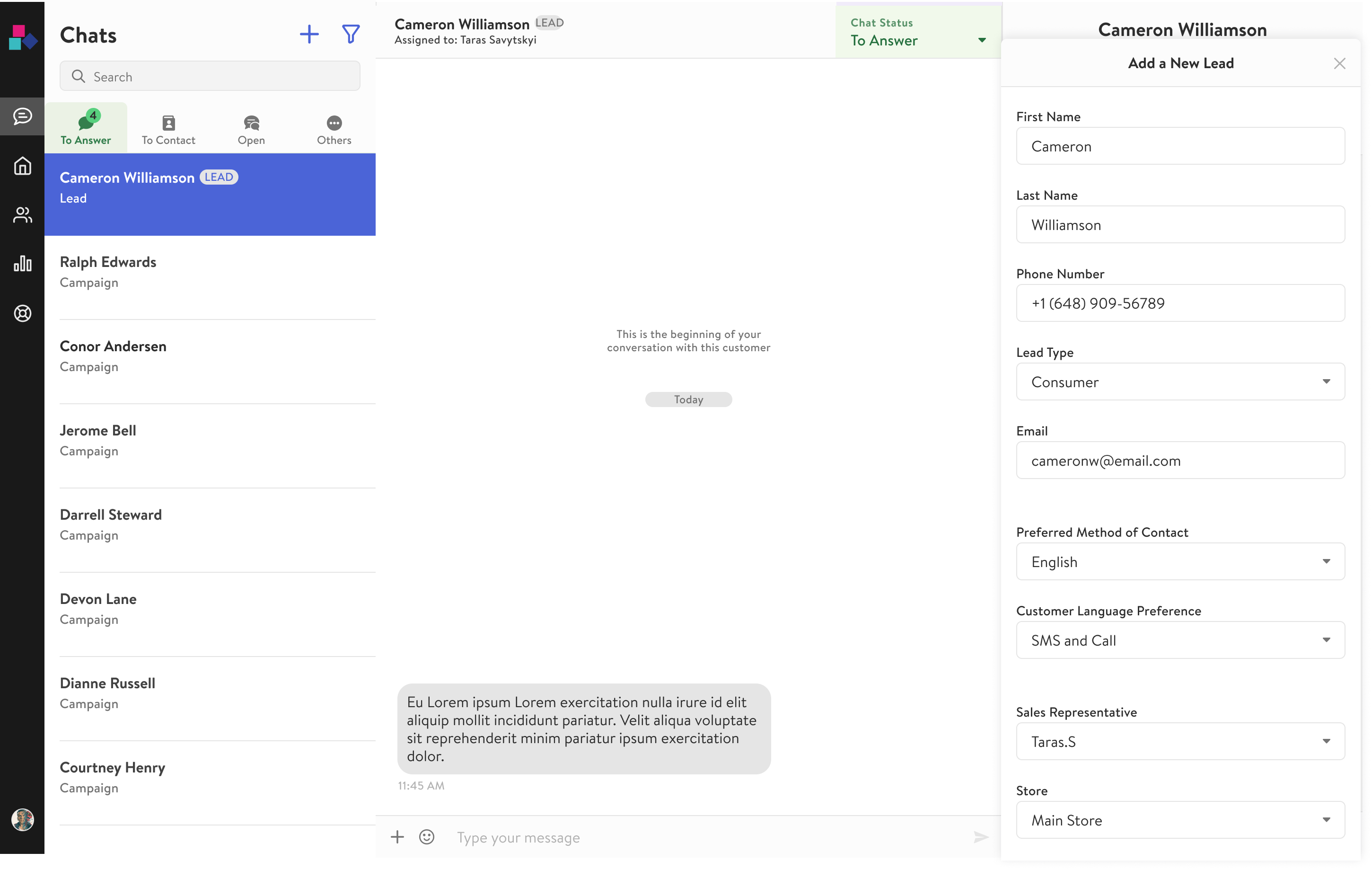
The wireframe above illustrates the ability to add a lead’s contact information to a customer database. Like above, since inbound leads were a major source of revenue for retail banks, clients needed to be able to retain the contact information of potential customers. This was to follow up with leads or seamlessly convert leads to a newly registered customer.
The success of the designed solution can be evaluated through two perspectives: product design and business. Although there is a certain objective aspect in user interface design, such as accessibility standards, most of the work is subjective. Such a subjective practice can be best evaluated through usability testing and user acceptance testing. In usability testing, a user independently follows instructions to complete tasks using the user interface. The usability of the user interface is then quantitatively evaluated through means such as a 7-point Likert scale for rating the design’s intuitiveness. For the Inbound SMS feature, the resulting average score was 6.8, so the design was deemed outstandingly intuitive. In user acceptance testing, a user independently uses the solution to verify and validate that the solution satisfies their needs and requirements. After testing with several users, it was evident that the solution satisfied all outlined needs and requirements.
From a business perspective, it must be considered whether the designed solution directly resulted in the acquisition of clients in the retail bank industry and if the revenue target was reached. Seeing as how Statflo was able to acquire a prominent retail banking client and surpassed the revenue target directly due to the Inbound SMS feature, the solution was a success in both aspects.
Through conducting user research, the feature that showed the most promise was the ability for inbound SMS messages to be received from unrecognized phone numbers in Statflo. Following intensive cross-functional collaboration and software development, a feature to address the problem space was released, successfully enabling targeted revenue growth for the company.
The original question this project set out to answer was: What is the best way to enable Statflo to acquire clients in a new industry sector and ultimately increase revenue? Through conducting extensive market and user research, applying product management best practices, and leveraging widely accepted tools, an optimal problem space within the retail bank industry was identified and resolved. The resulting design solution was a software feature within Statflo’s business messaging product, TextKit, that allowed for inbound SMS messages from unrecognized phone numbers to be received by sellers. The solution was successful in producing business value for Statflo, resulting in the acquisition of a client in the retail bank industry as well as surpassing the targeted revenue growth. Thus, the project overall was an astounding success with all outlined goals achieved.
"Nick is a natural user-centric product thinker; great at problem-solving and coming day in and day out with an innovative “outside the box” mentality. He’s an excellent writer, process-driven, self-managing, poses thoughtful questions, and was all-around a great addition to the team.
Nick executed his work with great quality and detail. He was able to show a wide range of versatile skills that made us comfortable to enable him to work on an entire Q3 roadmap feature that enabled the company break into new verticals and give him creative freedom to adjust Figma mock-ups for the sake of quick, agile stakeholder alignment.
From his first week, Nick showed proactiveness by jumping on above & beyond opportunities to move our team forward. His end-to-end execution of revitalizing our company’s User/Customer Interview Process would be a perfect example of this. I strongly recommend Nick to any Product team - he has tremendous potential and has the special ability to think at a high level and above his role."